Silicates from Renewable Resources
Pörner Bio-Silicate Technology
With Pörner Bio-Silicate Technology, you can efficiently and sustainably produce ultra-pure bio-silicates for a variety of applications. This advanced, patented technology extracts high-quality silicon compounds from rice hull ash for the global market.
This 3D model illustrates the overall concept and successive production steps of a typical Pörner Bio-Silicate plant, from processing rice hull ash (RHA) to producing the final bio-silicate product.
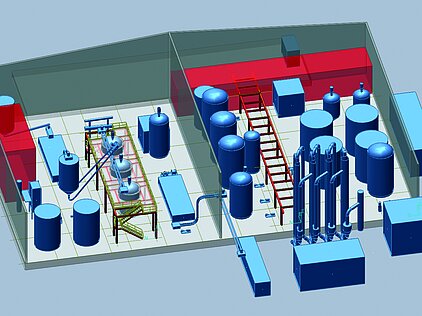


Technology Overview

Each grain of rice is enclosed in a hull, which provides perfect natural protection against external influences, yet it is considered waste in rice production. Rice hulls consist mainly of silicates and cutin, which is an enormous, largely untapped source of energy. Approximately 20% of the rice plant is hull. Due to their chemical composition, rice hulls decompose very slowly, releasing methane in the process, which is a serious environmental issue in many regions of the world.
The Pörner technology converts rice hulls into climate-friendly, renewable green energy in modern, highly efficient biomass power plants. The resulting rice hull ash contains approximately 90% silicon dioxide (SiO₂), which is processed further in the Pörner silicate plant into high-quality circular bio-silicate.
Silicate is a key raw material with countless applications. Sodium and potassium silicates, in particular, are essential products on every continent. The Pörner plant concept enables the production of both types of silicate using the same configuration.
Sodium silicates:
Significantly higher SiO₂/Na₂O weight ratios of up to 4.0 can be achieved for sodium silicates (unlike the hydrothermal process, which is limited to 2.6).
- Liquid sodium silicate (LSS): The SiO₂/Na₂O ratio ranges from 1.0 to 4.0, and the solids content can reach 37%
- Powdered sodium silicate (PSS): The SiO₂/Na₂O ratio ranges from 1.0 to 4.0, and the solids content is a minimum of 95%
Potassium silicates:
- Liquid potassium silicate (LPS): The SiO₂/K₂O ratio ranges from 1.0 to 2.6, and the solids content is up to 37%
- Powdered Potassium Silicate (PPS): The SiO₂/K₂O ratio ranges from 1.0 to 2.6, and the solids content is a minimum of 95%
By-product: Filter Cake (CC)
A filter cake, consisting mainly of residual carbon, SiO₂, and various trace elements, is generated as a by-product. It can be used in a wide range of applications, such as:
- Activated carbon filters (e.g. cleaning gaseous media streams)
- Soil conditioning (e.g. treatment of acidic soils, land reclamation)
- Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers
By-product: CO₂ Certificates
Compared to conventional silicate production processes, up to 900 kg of CO₂ per ton of solid silicate can be saved. With rising CO₂ certificate prices, this translates into a significant financial advantage.

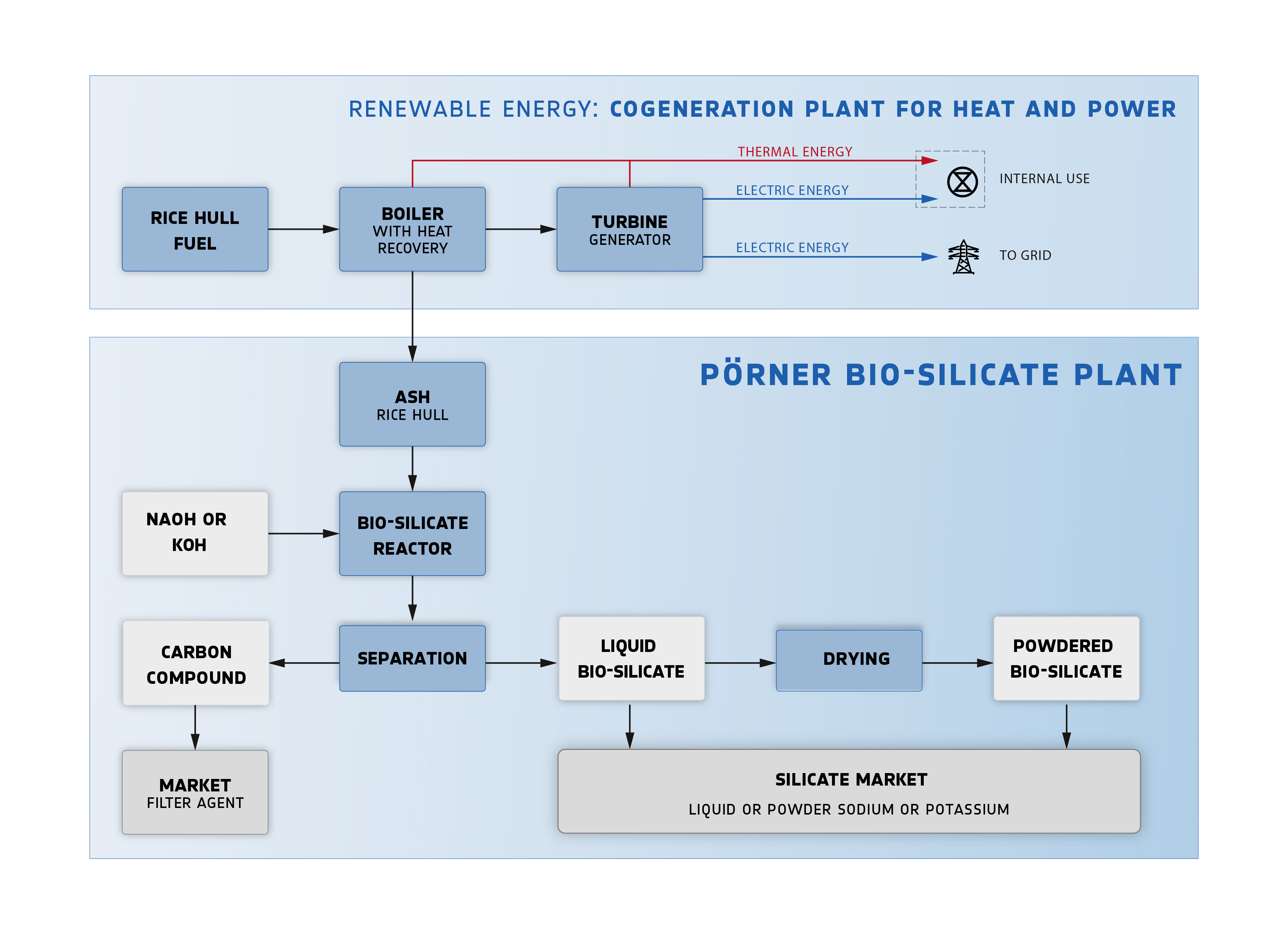
The technology...
- stabilizes the energy supply in rural areas and provides access to clean energy and sustainably produced products.
- addresses a major ecological problem by putting rice hulls to good use instead of leaving them to rot in open dumps or burning them in environmentally harmful ways.
- reduces the CO₂ footprint of silicate production by up to 70% compared to conventional processes.
- improves the quality and purity of bio-silicates, reducing impurities to one-tenth of those in conventionally produced silicates.
Economic efficiency…
- High-quality, sustainable, circular industrial raw material made from pure, amorphous SiO₂ commands higher market prices due to rising demand and the global shift toward green, sustainable products.
- Using rice hulls and their ash creates added value instead of generating disposal costs and a climate impact from natural decomposition.
- Rice hull-fired biomass power plants generate thermal energy in form of steam and produce electricity and amorphous silicon raw materials.
- The bio-silicate production plant for industrial and agricultural applications is far less complex than conventional process lines and can be built with a smaller footprint.
- The carbon compound generated as a bi-product of bio-silicate production can be profitably returned to agriculture.
Sustainability…
- As part of the rice plant, rice hulls represent a renewable natural resource available in millions of tons annually. Energy from renewable biological resources is generated in a climate-neutral way. Combined heat and power (CHP) ensures maximum energy efficiency.
- Combustion or gasification followed by silicate processing occurs at significantly lower temperatures than conventional production methods.
- The CO₂ footprint is reduced by up to 70% when combined with an energy supply from a biomass power plant compared to conventional production from sand.









The global market for silicates is growing rapidly. The market volume for sodium silicate is expected to grow from $6.40 billion in 2022 to $8.19 billion by 2029, which corresponds to an average annual growth rate of 3.6% during the forecast period. Currently, the fastest-growing segment is precipitated silica for tire production (“green tires”).
Silicates have diverse applications, ranging from bleaching agents in the paper industry to additives in detergents, paints, building materials, cosmetics, tires, and construction chemicals. Silicon can also be processed into eco-friendly fertilizers that enhance plant growth and health, increasing crop yield and quality by up to 25%.

Pörner operates a state-of-the-art demonstration plant in Freiberg, Germany. This plant is designed to determine and optimize the key process parameters of rice hull ash from various regions around the world.
According to customer specifications, the plant produces high-quality, sustainable, circular bio-silicates in liquid form from the supplied ash. Modern process and laboratory equipment allows for efficient analytical studies, as well as further process development and optimization.

Technology-Flyer
English

Mario Sleska
Business Development Bio-Silicates
Email: mario.sleska@poerner.at
Phone: +43 5 05899-618
Mobile: +43 664 80589618


